With a series of early pregnancy complications and several ill-health conditions, a soon-to-be mother experiences a roller coaster ride throughout her journey of pregnancy. From feeling nausea to experiencing labor pain a woman goes through a lot while she is pregnant.
One such condition is Polyhydramnios.
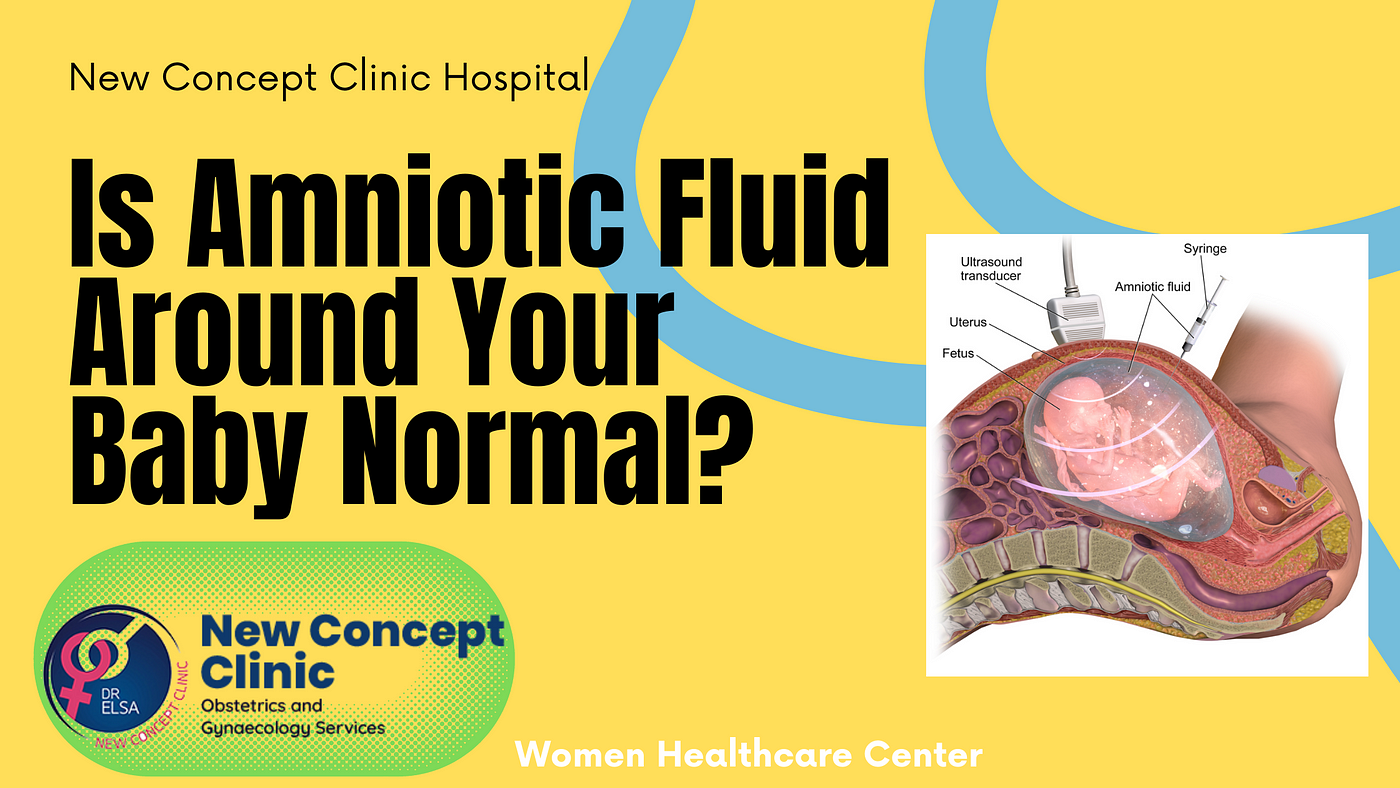
Polyhydramnios, also considered the Amniotic Fluid disorder, is a condition where the fluid in the amniotic sac surrounding your fetus is more than 2000ml. The fluid is said to start being produced around 12 days after conception with the purpose to support the baby inside the uterus and help develop their limbs, lungs, and other organs.
In general, the normal amount of amniotic to be present is 800ml noticeable at 34 weeks of pregnancy. As the pregnancy decreases the amount of amniotic fluid is said to be reduced to 600ml at 40 weeks of pregnancy period.
Causes of Polyhydramnios
The exact causes of polyhydramnios are sometimes not considered to be known but can be due to fetal, maternal, and other related causes like:
- Fetal cause: Fetal malformations, fetus swallowing amniotic fluid.
- Genetic abnormalities: Abnormal number of chromosomes.
- Cardiovascular defects: Heart diseases, shortness of breath, chest pain.
- Neural tube defects: Conditions like anencephaly and open Spina Bifida.
- Maternal cause: Uncontrolled diabetes in the mother, increase in fetal blood sugar, kidney problems.
- Carrying twins or triplets: Multiple pregnancies occur in 8–10% of women.
- Anemia: Fetal anemia cases in 1–11 of cases.
- Viral infections: Parvovirus B19, rubella, cytomegalovirus.
Signs of Polyhydramnios
In most cases, there are no symptoms or there are only mild symptoms to which women do not pay much. The symptoms are:
- Breathlessness while lying down
- Palpitation
- Larger abdomen
- Heartburn
- Constipation
- Pressure in belly
- Swollen feets
- Weight gain
Differential Diagnosis of Polyhydramnios
The development of polyhydramnios can appear at any point in pregnancy. With the growth of it comes higher chances of developing more serious pregnancy problems. The diagnosis of Polyhydramnios is done by many different investigations like:
- Ultrasound: Polyhydramnios is detected using two methods of ultrasound: Amniotic fluid index and single deepest pocket.
- Blood tests: The blood test includes testing of ABO and Rh blood grouping and measuring the sugar levels.
- Laboratory tests: The laboratory tests include several screenings like blood glucose, maternal infection, etc.
- Fluid test: The fluid test is carried out to make the estimation of alpha-fetoprotein.
Treatment and Management of Polyhydramnios
The treatment and management process of polyhydramnios depends on the extent of its underlying cause and the severeness of the condition.
Mild polyhydramnios is reduced by itself, the patient is said to be on complete bed rest for a few days.
Severe polyhydramnios is treated in the hospital by removing amniotic fluid at regular intervals. If in any case, the pregnancy is of more than 37 weeks, then the process is followed by the delivery of the fetus.
Closing words
In a conversation with Dr. Elsa, a Mediclinic Obstetrician and Gynaecologist the occurrence of amniotic fluid is normal till it does not become excessive. Prevention of Polyhydramnios is easy and can be carried out by early detection of polyhydramnios, control of maternal diabetes, genetic counseling, and other effective measures.
No comments:
Post a Comment